Diabetes mellitus is one of the important socio-economic problems caused both by the increase in morbidity and disability, and mortality of people of working age. It is known that the endocrine and digestive systems are closely interconnected in the body. Despite a large number of works devoted to visceral lesions in diabetes mellitus, the issue of pathology of the biliary system remains unresolved.
We examined 75 patients and analyzed 268 outpatient charts of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus who underwent examination and treatment in the endocrinology and gastroenterology departments of the Stavropol Krai Clinical Hospital for the period from 2018 to 2022.
The predominance of women over men was observed in the examined groups of patients.
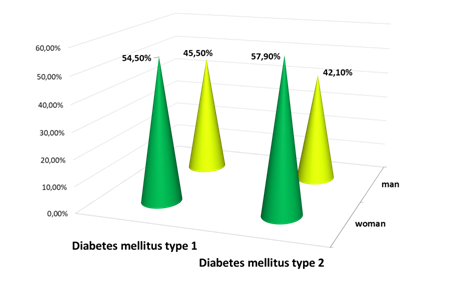
Diagram.1 Distribution of patients with DM depending on gender.
Exclusion criteria were patients with insulin resistance, as well as with comorbidities that could affect the functional state of the liver and biliary tract.
The comparison group consisted of 58 patients comparable in age and sex with biliary system pathology without concomitant diabetes mellitus.
The examination of the patients had a complex character and included general clinical and special parts and was carried out during the first days of hospitalization, before the treatment and against the background of the therapy.
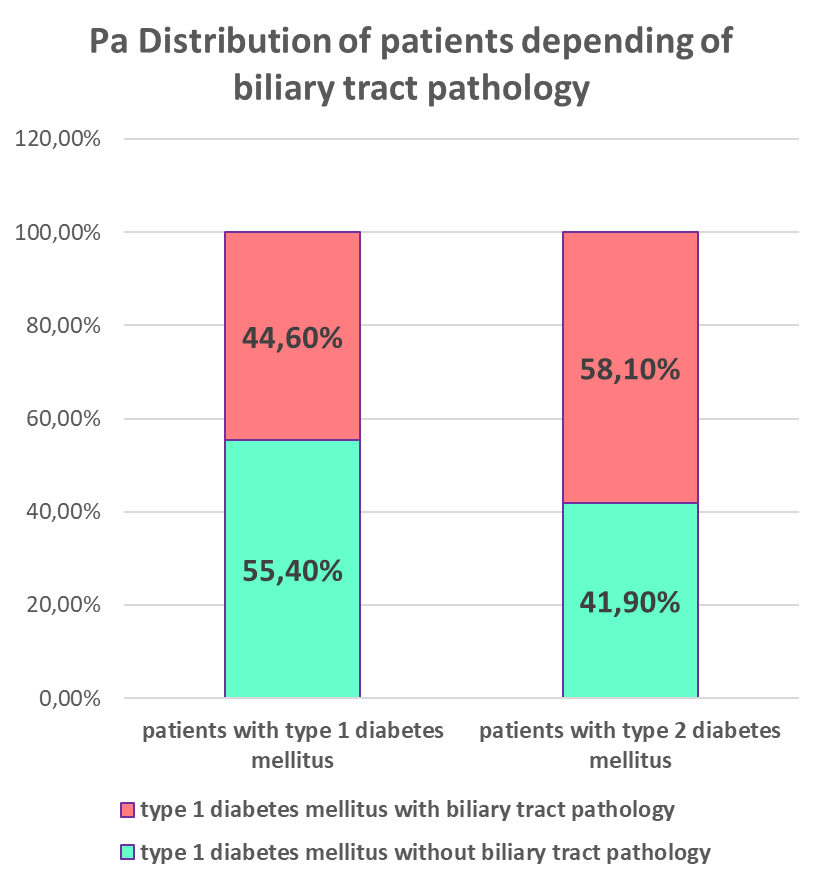
On the basis of clinical and laboratory-instrumental examination 24% of patients were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus type 2 was diagnosed in 76 % of patients, and in this group the concomitant pathology of biliary system was more pronounced.
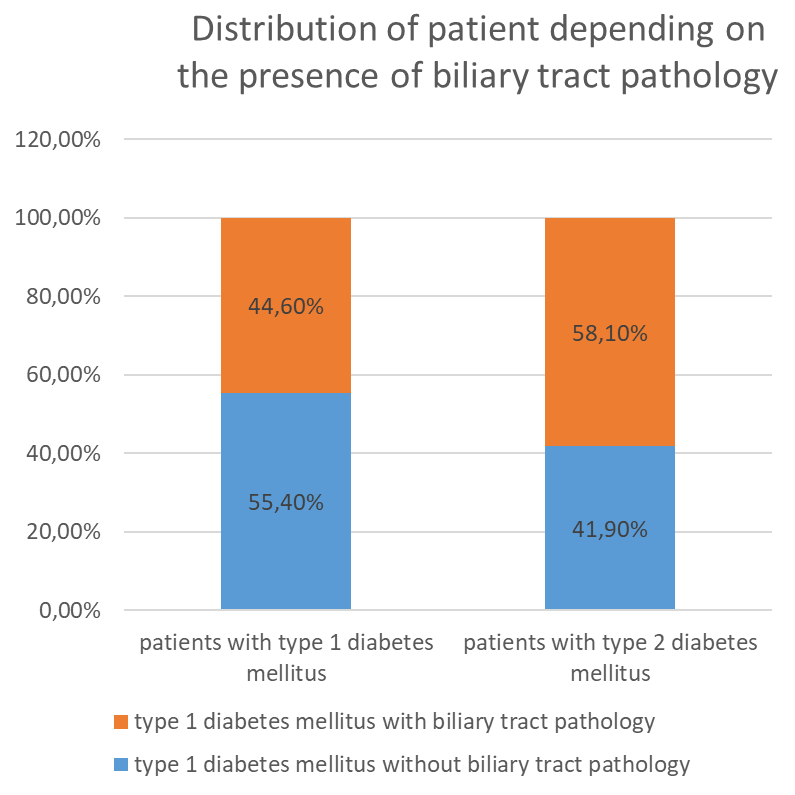
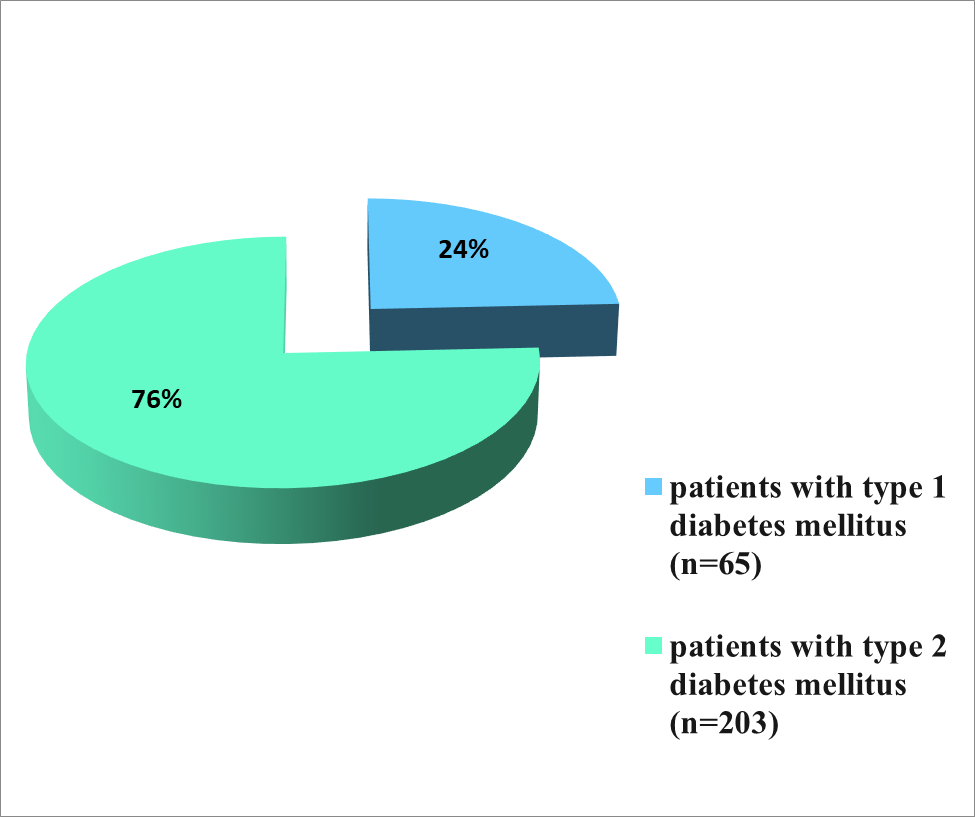
Diagram. 2,3 Distribution of patients taking into account the type of diabetes mellitus and the presence of GI diseases.
In the clinical picture of patients with diabetes mellitus of both type 1 and type 2 with concomitant pathology of biliary tract, low-intensity pain and heaviness in the right subcostal region, intensified after meals, almost constant bitterness in the mouth, belching of air, alternation of constipation and diarrhea were significantly more frequent than in the comparison group. In the comparison group these complaints were also detected, but occurred less frequently.
Stool disorder was observed in all groups of the examined: in patients with DM - sideways, while in half of patients with biliary tract pathology without DM - constipation prevailed.
Clinical manifestations in patients with DM with concomitant biliary pathology of CCBH and in patients with biliary diseases without DM.
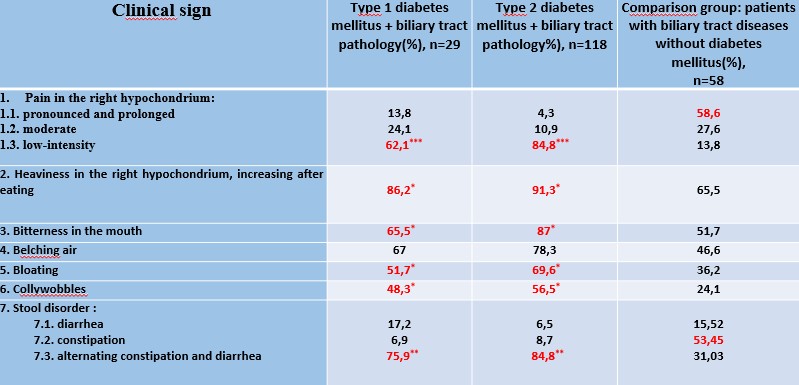
Table 1. Clinical manifestations in patients with diabetes mellitus with concomitant pathology of the biliary tract, chronic acalculous cholecystitis and in patients with diseases of the biliary tract without diabetes mellitus.
At palpation of the abdomen in patients with diabetes mellitus it should be noted less pronounced soreness in the area of the right subcostal region, as well as weak positive bladder symptoms, which were more intense in the comparison group.
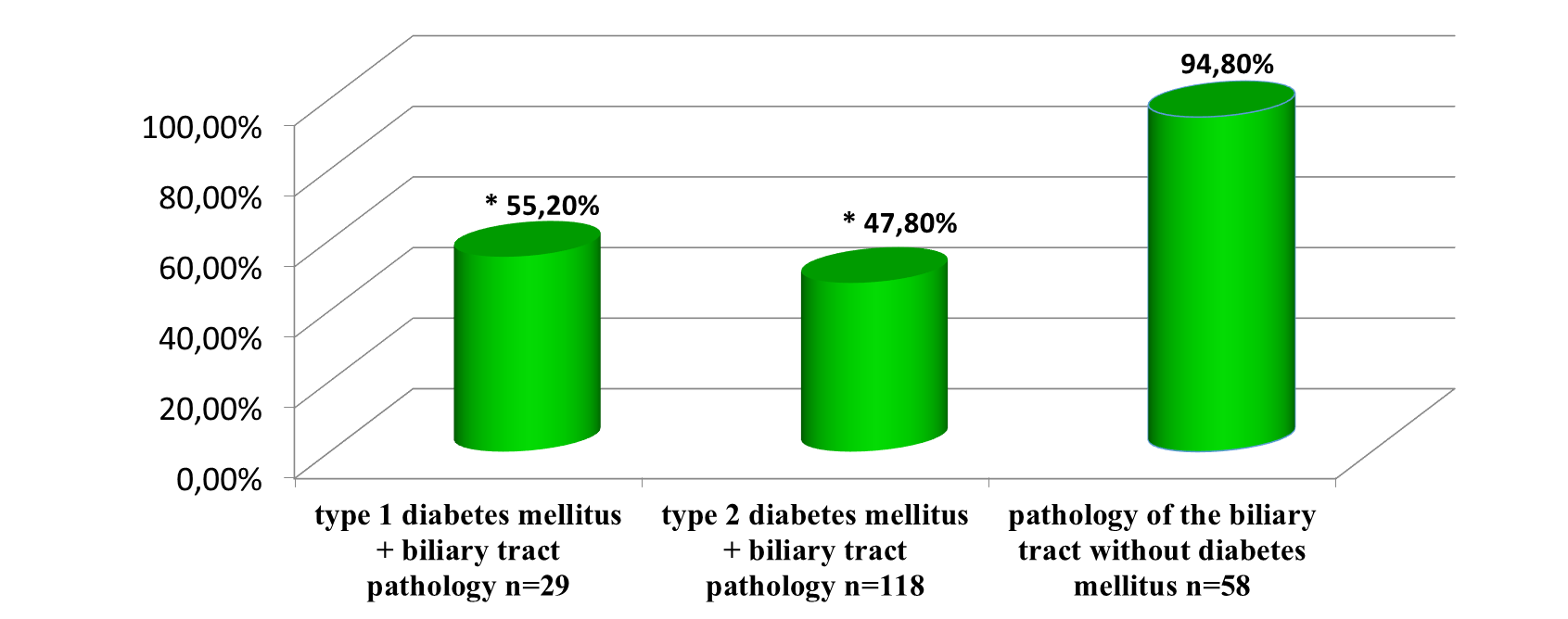
Figure 4. Presence of right subcostal painfulness and positive vesicular symptoms.
When analyzing the pathology of biliary tract in the studied groups, an increase in the number of functional disorders in patients with diabetes mellitus was revealed, more pronounced in patients with DM type 2, compared to the comparison group. Organic pathology (chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis) were detected without pronounced predominance.
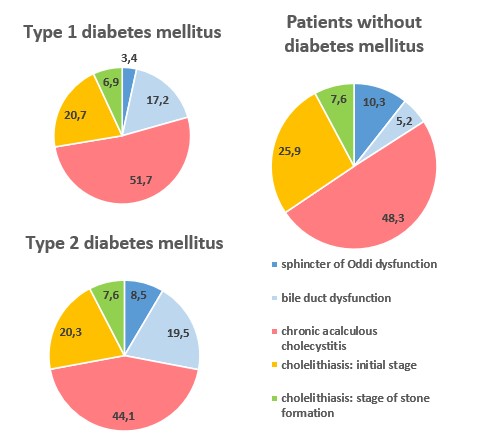
Graph 5,6. Distribution of biliary tract pathology in patients with and without diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2.
When analyzing the clinical course of biliary tract pathology in patients with DM a latent and monotonous course with moderate complaints prevailed. While in the comparison group in the majority of cases recurrent course with moderate pain and dyspepsic syndromes was noted, which amounted to 84,5 % of the total number of this group.
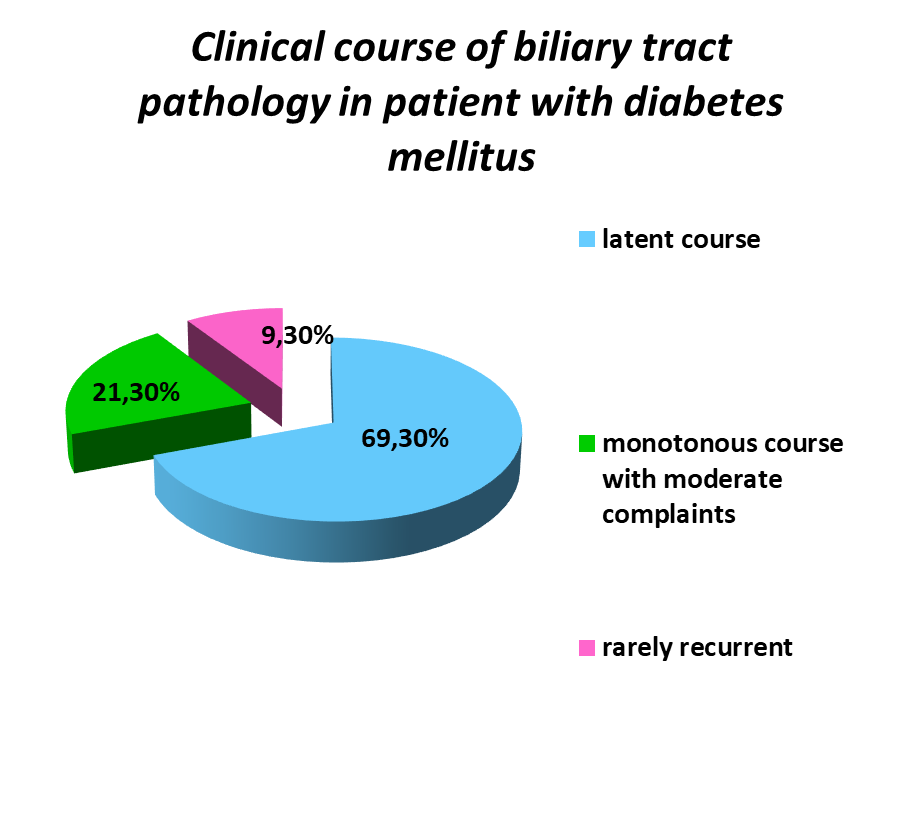
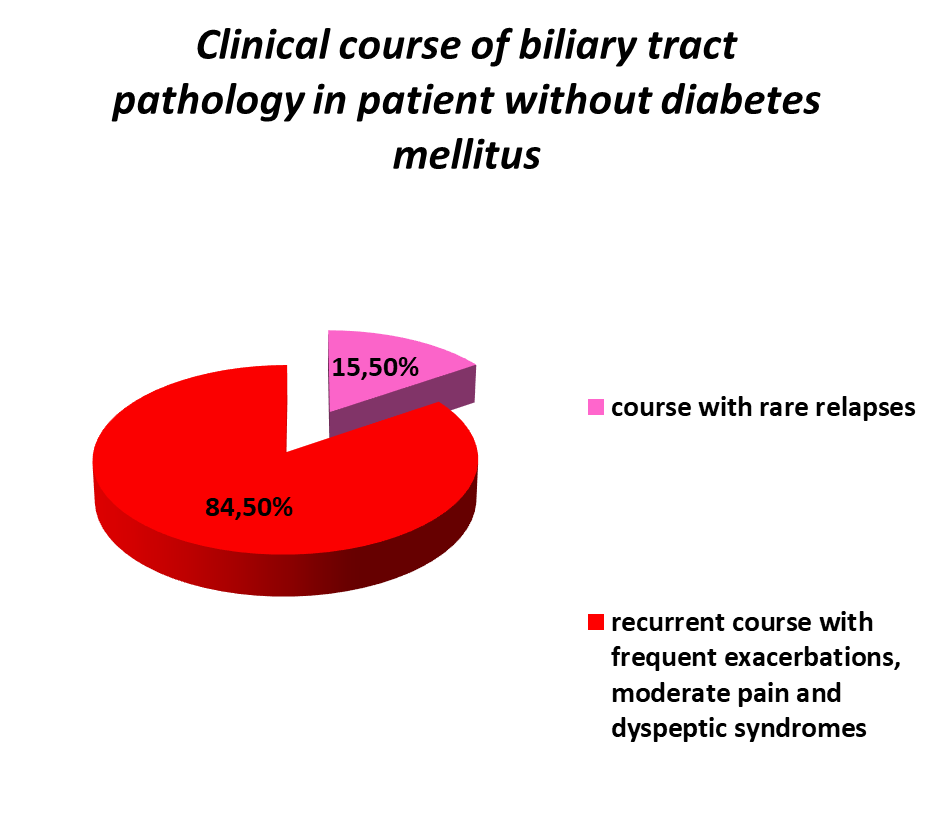
Graph. 7, 8. Distribution of patients taking into account the course of GI pathology.
All patients were treated according to the principles of "Biliary Continuum".
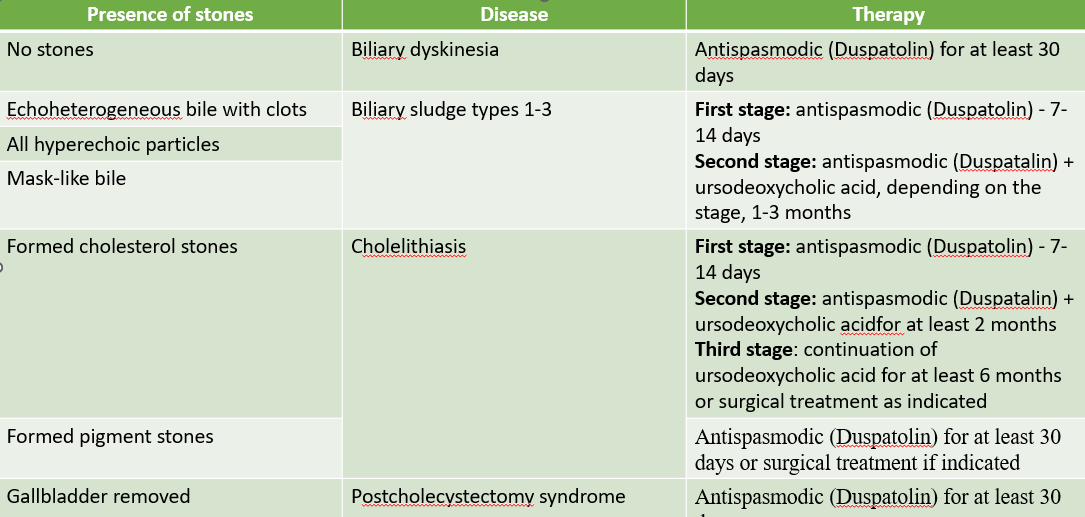
Fig. 1 Schemes of therapy of biliary continuum diseases.
In 3 years after the appointment of therapy in the studied groups there was a redistribution of pathology towards an increase in the number of patients with cholelithiasis in the groups of patients with diabetes mellitus, more pronounced in patients with type 2 DM, while in the comparison group the ratio of the studied pathology practically did not change.
What can be more clearly seen on the presented diagram (yellow and green blocks on even columns are the indicators of LCDD development).
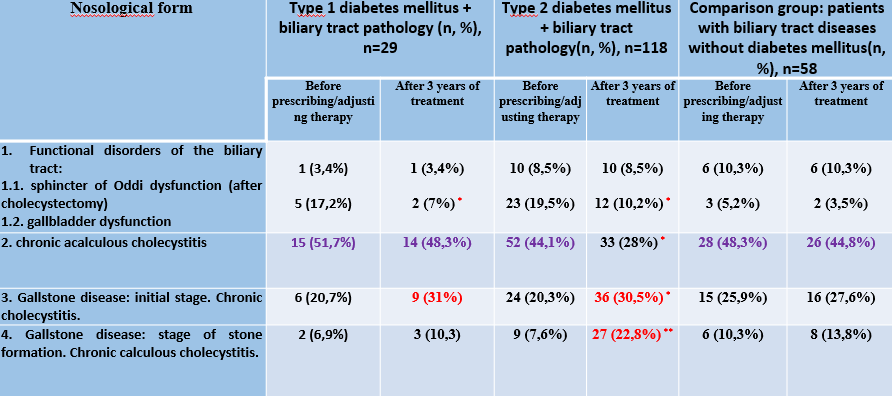
Table 2. Dynamics of GI pathology progression in patients with DM and in patients with GI diseases without DM.
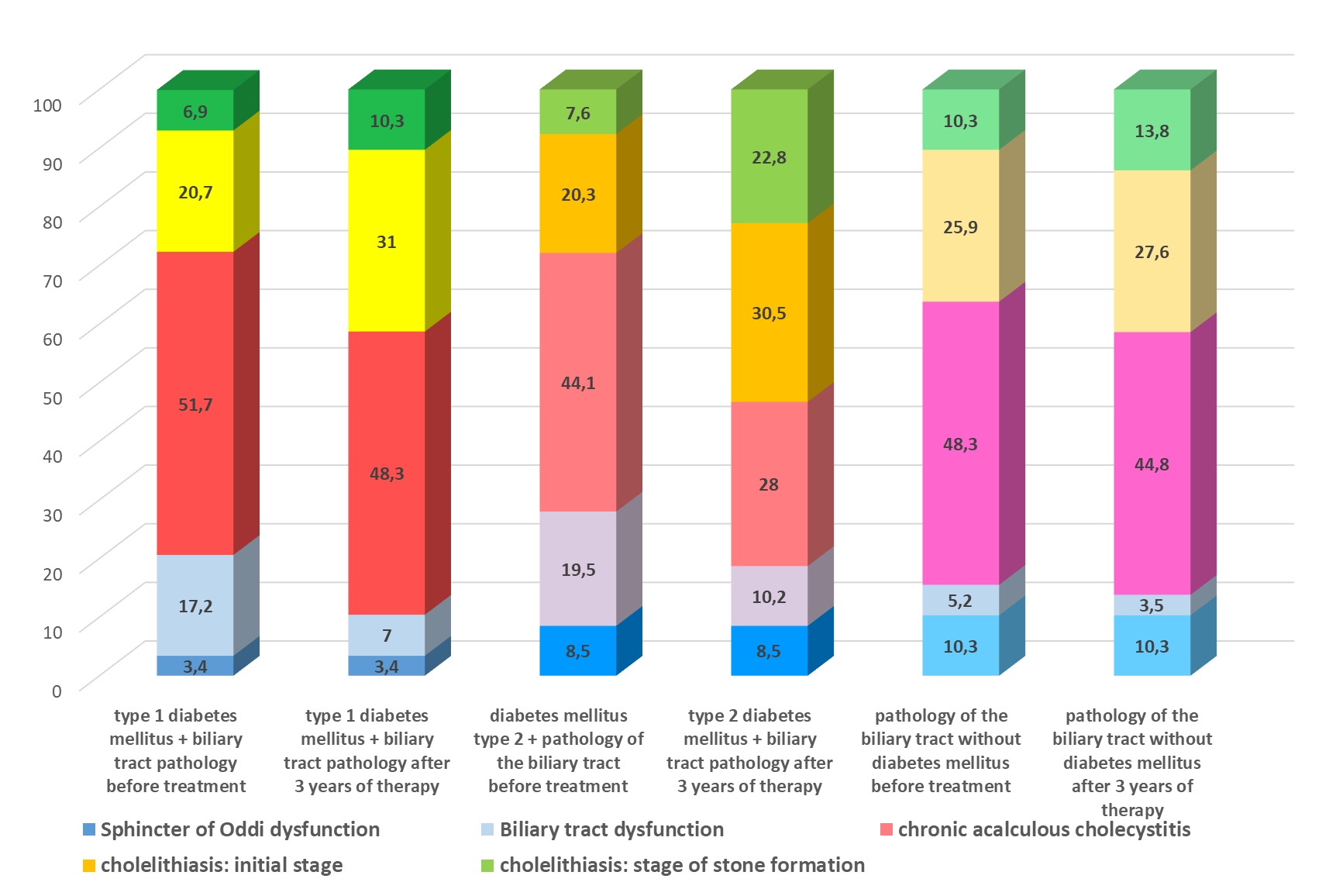
Graph. 9 Dynamics of progression of biliary tract pathology in patients with diabetes mellitus and in patients with biliary tract diseases without diabetes mellitus (in%)
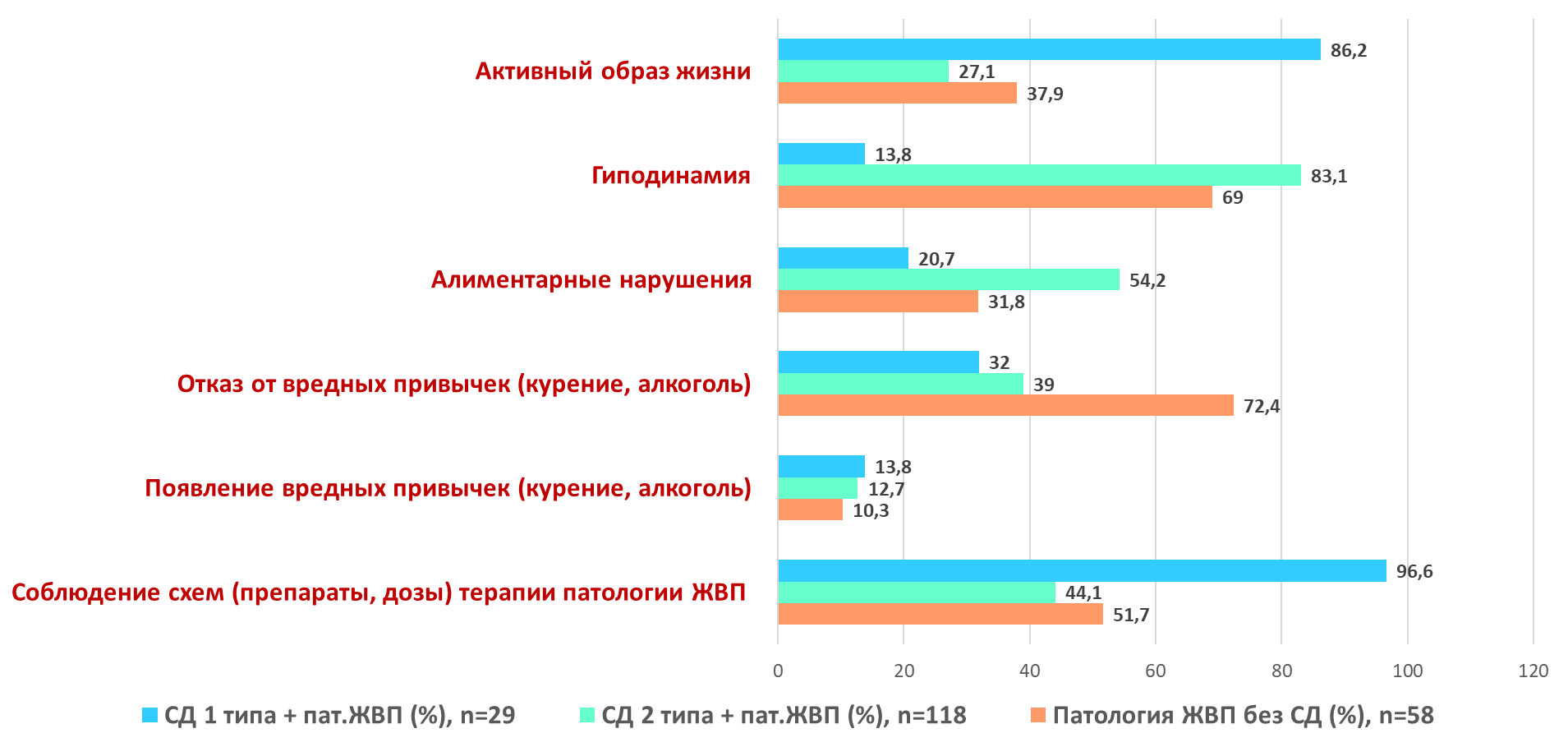
During the questionnaire survey it was found that in the groups of patients with diabetes mellitus for 3 years against the background of the conducted therapy there was an increase in the number of factors unfavorably influencing the progression of biliary pathology.
Diagram 10. Factors influencing the dynamics of GI pathology during treatment (in %)
The following conclusions were made on the basis of the study:
1) Diseases of biliary tract occur in patients with diabetes mellitus with high frequency.
2) Functional disorders of biliary tract in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus are more frequent compared to the groups of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and without concomitant diabetes mellitus.
3) Clinical manifestations of biliary tract pathology in patients with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus are less pronounced in comparison with this pathology in patients without concomitant diabetes mellitus.
4) In patients with diabetes mellitus on the background of the current therapy there is a more pronounced progression of biliary pathology compared to the group of patients without diabetes mellitus.
5) Early detection of biliary system disorders and prevention of risk factors of biliary pathology progression in patients with DM can contribute to their timely correction and prevention of complications development.
Список литературы
- Algorithms of diagnostics and treatment of endocrine system diseases under the editorship of I. I. Dedov. I. Dedov. - Moscow, 1995 - 335-336 p.
- Ametov A.S., Endocrinology [Electronic resource] / A.S. Ametov, S.B. Shustov, Y.Sh. Halimov, - M. : GEOTAR-Media, 2016 - 24-26 p.
- Clinical recommendations. Pancreas transplantation, presence of transplanted pancreas, pancreas graft die-off and rejection - 293-295 p.
- Antsiferov M.B. Modern concepts in the training of patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus. 1999 - 176 c.
- National statistical report on diabetes mellitus, 2014 - 233 c.



